Decoders#
Decoders are logic circuits that accept a multi-bit input (such as the bits of a binary number) and activate the relevant output from a larger set. For example, in the memory system of a computer each register has its own unique address. when it receives the address, a decoder can send an enable signal to one specific register to be read/written to while the others are not affected.
Pictured below is a 2-bit binary decoder. It takes in the binary number \(AB\) and activates (sets Hi) exactly one of the outputs while the others remain Low. This particular decoder is referred to as a “1 of 4” decoder because only one of the four possible outpus is active at a time.
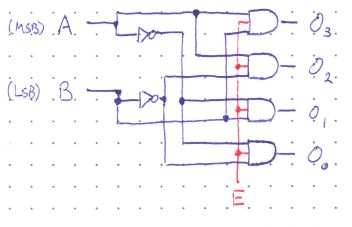
Ignoring the red E input for the moment, the dcoder’s logic is fairly straightforward. \(O_3\) will be High only when both \(A\) and \(B\) are High (representing the number three in binary). Similarly, \(O_2\) will be High only when \(AB = 10\), \(O_1\) when \(AB = 01\), and \(O_0\) when \(AB = 00\). There are four different combinations of input values, and a different output will be high for each of those combinations. Thus the input is “decoded”.
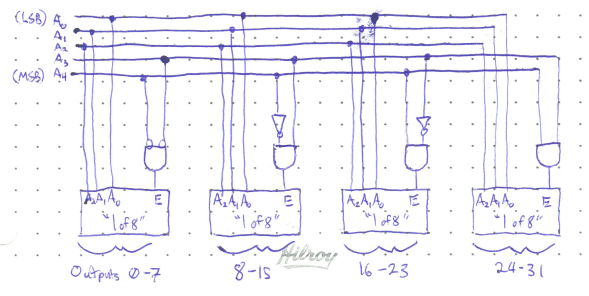
Often, a third Enable input is included (coloured red in the diagram) to restrict outputs to only be active when the Enable input is High. This functionality is useful for combining small decoders together to make a larger one. For example, below is a “1 of 32” decoder ,ade from four “1 of 8” decoders. The two most significat bits control the logic at the Enable inputs, ensuring that only one of the decoders have an active output.
BCD Decoders#
Binary Coded Decimal (BCD) is another common way of encoding numbers. In this system, each decimal digit is represented by a 4-bit binary number. For example, 42 would be encoded as 0100 0010. It can be very convenient since humans use the decimal system. This system is commonly used in calculators, microwaves, phones, or any other system where digits are entered by or displayed to humans. A common decoder is thus the BCD-to-Decimal of “1 of 10” decoder.
Similarly, BCD is often decoded in a specific manner for an LED component called a seven segment display. If you’ve ever looked at a digital clock or a microwave, you will recognize the blocky digits formed by seven lines that can light up. These lines are labelled \(abcdefg\) starting at the top and proceeding clockwise, with the final \(g\) in the middle. A BCD-to-7Segment decoder will have outputs for each segment, controlling the lights to form the appropriate digit.
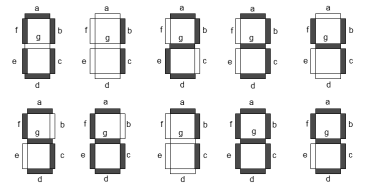
Be aware though, that there are two types of 7-segment displays: Common Anode where all seven LEDs share the same high voltage pin and thus will be turned on by a Low output from the decoder pin, and Common Cathode where the LEDs share a common ground and the decoder output needs to be High to activate the LED. Make sure you purchase the decoder that matches your display type.
